In summary, calculating capital expenditures is an integral part of financial analysis and decision-making for businesses. It provides valuable insights into the financial health of the company, helps in budgeting and financial planning, assesses investment opportunities, and supports long-term growth strategies. By accurately calculating and analyzing capital expenditures, businesses can optimize their resource allocation, improve operational efficiency, and drive sustainable growth. Understanding and tracking capital expenditures is crucial for businesses to make informed financial decisions. It helps management evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of different projects, assess the financial health of the company, and plan for future growth and expansion. By analyzing the capital expenditure data, companies can identify trends, make appropriate budget allocations, and ensure efficient utilization of resources.
Where can I find capital expenditures in financial statements?
- It provides a foundation for evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of capital deployment and contributes to strategic decision-making.
- On the other hand, growth capital expenditure focuses on investments aimed at expanding a company’s operations, increasing production capacity, or entering new markets.
- There are various factors that drive capital expenditure decisions, including the need to replace outdated equipment, expand production capacity, or improve operational efficiency.
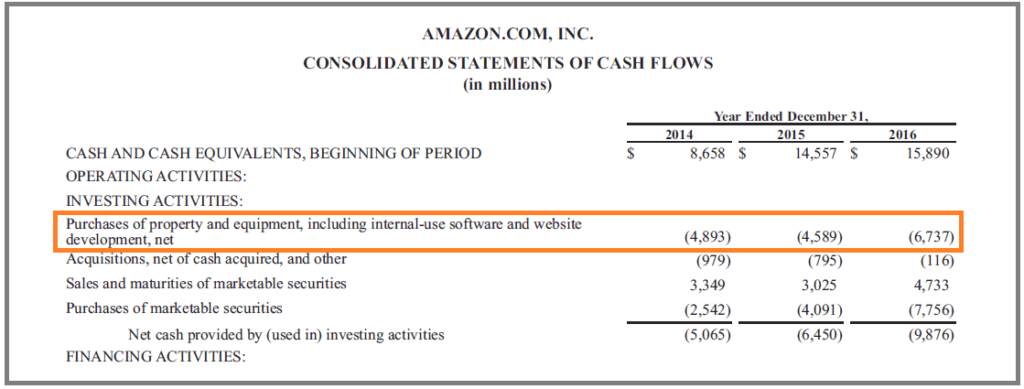
- Any spending on new server equipment and storage held in-house would be considered CapEx.
- However, you can depreciate or amortize the cost of the asset over its useful life.
- It allows you to evaluate the scale of investment, assess the effectiveness of asset management, and understand the company’s strategic priorities.
The thinking was that these expenses are necessary to generate revenue on a day-to-day basis. By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the capital expenditure of a company. Capital expenditure plays a crucial role in driving business growth and competitiveness. It enables companies to enhance their capabilities, innovate, and stay ahead of the competition in the market.
Cost estimation
CapEx helps to augment a company’s productive capacity, increase efficiency, or enhance competitiveness. These expenditures affect the organization positively over time by enhancing growth rates, profitability levels, and operational abilities. The resources for the capital expenditure are normally determined using crucial factors such as ROI, potential cash flow variance, risk assessment, and the overall financial soundness of the investment. Capital expenditures are long-term investments made by a company in order to increase its current capacity or improve its future performance.
Best Practices for Efficient Capital Expenditure Budgeting
On the other hand, buying a few new office chairs wouldn’t be a capital expenditure. It’s a minor purchase that doesn’t affect long-term growth or produce an asset. For example, new computers for a company’s office are an item of capital expenditure. They’re a considerable expense (often in the tens of thousands for just a few units) and the type of purchase that only occurs once every few years. Operating expenditure, also known as “OpEx” or Operating Expense, are those expenses necessary for daily business operations, generally including anything with a useful life of less than a year. Broadly speaking, this includes expenses relating to buying, updating, repairing, or improving a “non-current asset” (aka “fixed asset”).
Although it is a cost incurred by the company, it does not appear immediately on the income statement. Instead, the asset is depreciated over many years according to its useful life. Capital Expenditure (CapEx) refers to the funds a company invests in long-term assets, such as property, equipment, and infrastructure.
For example, if the company is disposing of underutilized or outdated assets to free up capital for new investments or reduce costs, negative CAPEX could be a positive sign. However, if the company is selling off core assets needed how to calculate capex from balance sheet for its operations, negative CAPEX could be a warning sign of potential long-term issues. This gives companies more money to invest in operations and other income-generating activities instead of spending that money on taxes.
It’s important to note that the total capital expenditures should be analyzed in relation to the company’s overall financial performance, industry benchmarks, and long-term growth objectives. It provides a foundation for evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of capital deployment and contributes to strategic decision-making. By summing the net book value of existing assets with the value of additional capital expenditures, you will arrive at the total amount invested in long-term assets during the reporting period. Depreciation is a method of allocating the cost of an asset over its useful life. It reflects the reduction in value and the wear and tear that the asset experiences as it is used in the company’s operations.
To determine the historical cost, refer to the balance sheet and locate the values for each long-term asset. The historical cost information can usually be found in the asset section or in related footnotes. It is important to analyze each asset individually and record its historical cost. It is possible for a company to have negative CAPEX, although it is relatively uncommon. Negative CAPEX typically occurs when a company sells or disposes of its long-term assets, resulting in a reduction in its PP&E balance. That said, a significant build-out of a new location might be considered CapEx since the project focuses on growing the business—and the office chairs could be rolled into that.
Capital expenditures play a pivotal role in a company’s free cash flow (FCF) and valuation. FCF represents the cash generated by a company’s core operations after deducting both operating expenses and capital expenditures. Higher CapEx can reduce FCF, impacting a company’s financial flexibility and ability to pay dividends or reduce debt.
Factors driving capital expenditure decisions include the need to replace outdated equipment, expand production capacity, and improve operational efficiency. Companies evaluate potential benefits and returns on investment before committing to CapEx projects[1]. CapEx is recorded on the balance sheet as an asset, while OpEx is recorded on the income statement.
